While a plethora of high-quality text-to-image diffusion models (Ramesh et al. 2022; Rombach et al. 2022; Podell et al. 2024) emerged in the last few years, credit mostly goes to the tremendous engineering efforts put into them. The fundamental theory behind them however, remained largly untouched – well, untill recently. The traditional “markov-chain” (Ho, Jain, and Abbeel 2020) or “SDE” (Song et al. 2021) perspective is now being replaced by an arguably simpler and flexible alternative. Under the new approach, we ditch the usual notion of a stochastic mapping as the model and adopt a deterministic mapping instead. Turns out that such model, although existed, never took off due the absense of a scalable learning algorithm. In this article, we provide a relatively easy and visually guided tour of “Flow Matching”, followed by ideas like “path straightening” & “reflow”. It is worth mentioning that this very idea powered the most recent version of Stable Diffusion (i.e. SD3 by Esser et al. (2024)).
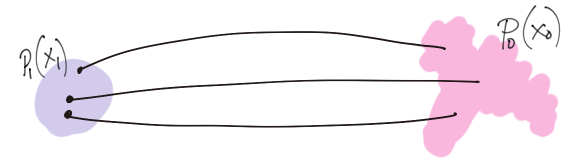
Every scalable generative model follows a “sampling first” philosophy, i.e. they are defined in terms of a (learnable) mapping (say
The learning objective is crafted in a way that the
Brief overview of Diffusion Models
The generative process
Although there are mutiple formalisms to describe the underlying theory of Diffusion Models, the one that gained traction recently is the “Differential Equations” view, mostly due to Song et al. (2021). Under this formalism, Diffusion’s generative mapping (in Equation 1) can be realized by integrating a differential equation in time

where
1 Knowns as the forward process marginal
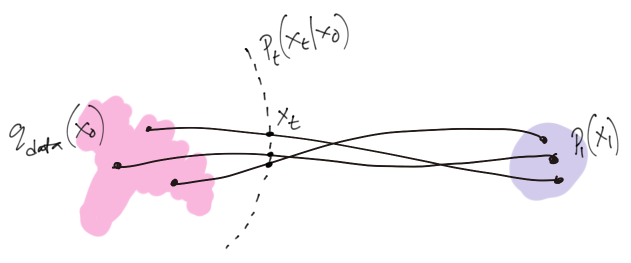
The relationship between
Despite being able sample
2 The ‘score’ of the marginal
The learning objective
A parametric neural function
It was proved initially by Vincent (2011) and later re-established by Song et al. (2021) that using
3 Please note that
Matching flows, not scores
The idea of re-interpreting reverse diffusion as “flow”4 stems from a holistic observation. Note that given Equation 3, an ODE dynamics is guaranteed to exists which induces a deterministic mapping from noise to any given data distribution. In diffusion model’s framework, we were only learning a part of the dynamics – not the dynamics itself.
4 This term comes from Continuous Normalizing Flows (CNFs)
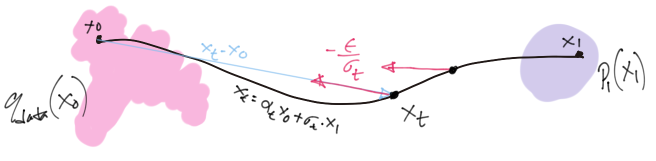
A deterministic model
Following the observation above, we can assume a generative model realized by a deterministic ODE simulation, whose parametric dynamics subsumes
Turns out, models like Equation 9 have already been investigated in generative modelling literature under the name of Continuous Normalizing Flows (Chen et al. 2018). However, these models never made it to the scalable realm due to their “simulation based”5 learning objective. The dynamics is often called “velocity”6 or “velocity field” and denoted with
5 One must integrate or simulate the ODE during training.
6 It is a time derivative of position.
7 .. or as it is now called, the ‘Flow Matching’ loss
Upon inspecting the pair of Equation 8 and Equation 6, it is not particularly hard to sense the existance of an equivalent ‘velocity matching’ loss7 for the new flow model in Equation 9.
An equivalent objective
To see that exact form of the flow matching loss, simply try recreating the ODE dynamics in Equation 8 within Equation 6 by appending some extra terms that cancel out
The expression within the first set of parantheses ( .. ) is equivalent to what now call the parametric velocity/flow or
To summarize, the following is the general form of flow matching loss
In practice, as proposed by many (Lipman et al. 2022; Liu, Gong, and Liu 2022), we discard the weightning term just like Diffusion Model’s simple loss popularized by Ho, Jain, and Abbeel (2020). We may think of
While the learning objective regresses against
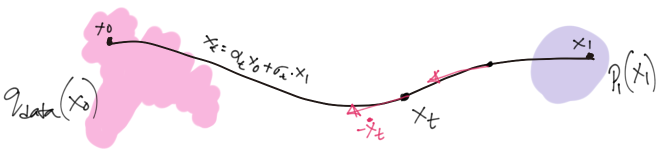
The minima & its interpretation
The loss in Equation 10 can be shown to be equivalent8 to
8 Their gradients are equal, but the losses are not.
which implies that the loss reaches its minima9 when the model perfectly learns
9 This is a typical MMSE estimator.
Hence,
The forward stochastic paths
10 cannot have multiple value at one given point
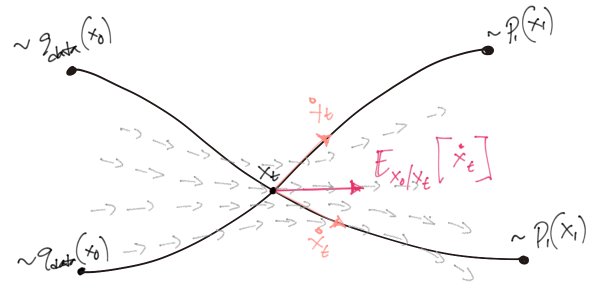
The optimally learned generative process (Equation 9) can therefore be expressed as
Straightening & ReFlow
With the general theory understood, it is now easy to concieve the idea of straight flows. It simply refers to the following special case
which implies the forward process and its time derivative to be
What is important is the stochastic velocity is independent of time11 and the
11 Not “constant” – it still depends on data
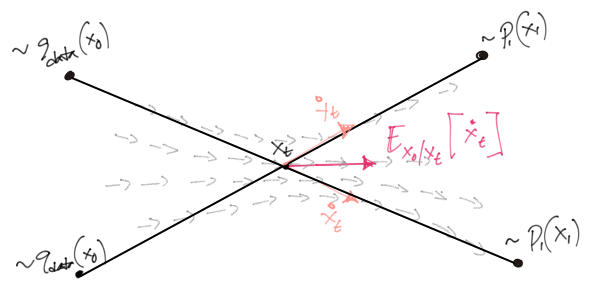
This however, does not mean that the learned model will produce straight paths – it only means we’re supervising the model to follow a path as straight as possible. An analogous illustration was provided in Liu, Gong, and Liu (2022) which is a bit more descriptive.
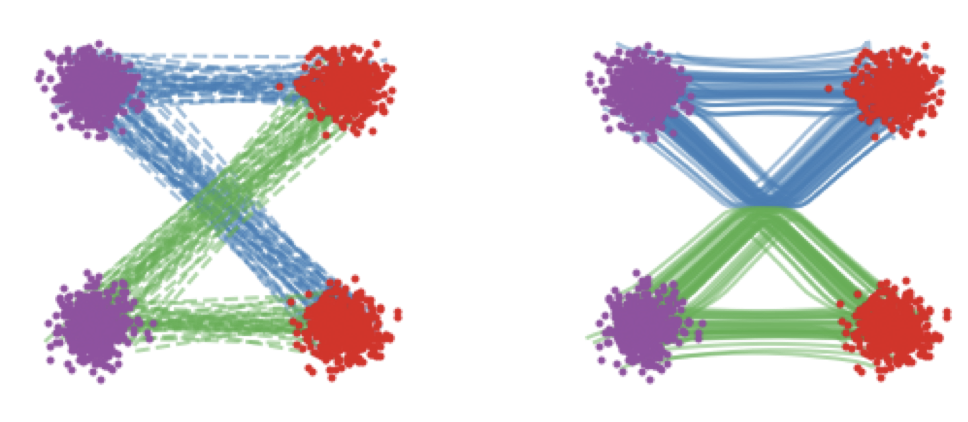
This learning problem (Equation 11) effectively turns an independent stochastic ‘coupling’
It can be proved that the samples
The proof uses the following
- The fact that
- Convex functions can be exchanged with
- Assumes our model learns the perfect
- Law of iterated expectation.
Please see section 3.2 of Liu, Gong, and Liu (2022) for more details on the proof.
Reflow
The process of rectification however, does not guarantee (as you can see in the above figure) the new coupling to have straight paths between each pair. Liu, Gong, and Liu (2022) suggested the “Reflow” procedure, which is nothing but learning a new model using the samples of
The ‘reflow’-ed coupling
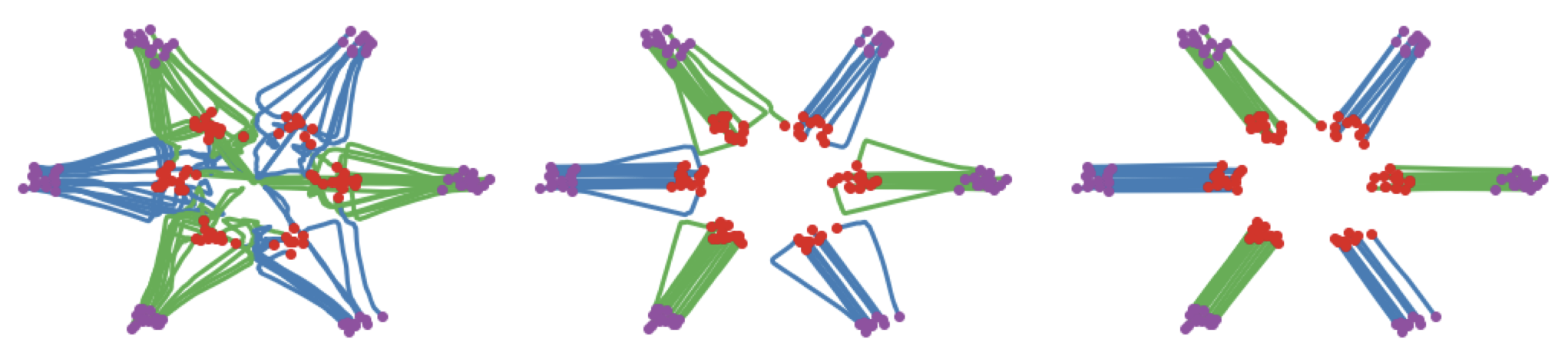
In this article, we talked about Flow Matching, Rectification and Reflow – some of the emerging new ideas in Diffusion Model literature. Specifically, we looked into the theoretical definitions and justifications behind the ideas. Despite having an appealing outlook, some researchers are skeptical of it being a special case of good old Diffusion Models. Whatever the case maybe, it did deliver one of the best text-to-image model so far (Esser et al. 2024), pehaps with a bit of clever engineering, which is a topic of another day.
References
Citation
@online{das2024,
author = {Das, Ayan},
title = {Match Flows, Not Scores},
date = {2024-04-26},
url = {https://ayandas.me/blogs/2024-04-26-flow-matching-strightning-sd3.html},
langid = {en}
}